Explore the characteristics and industrial applications of laser welding machines
Laser welding technology has transformed manufacturing processes across multiple industries by offering precision, speed, and versatility. This advanced joining method uses concentrated laser beams to fuse materials with minimal heat-affected zones, making it ideal for applications requiring high-quality welds. Understanding the core characteristics and industrial applications of laser welding machines helps businesses evaluate whether this technology aligns with their production needs and quality standards.
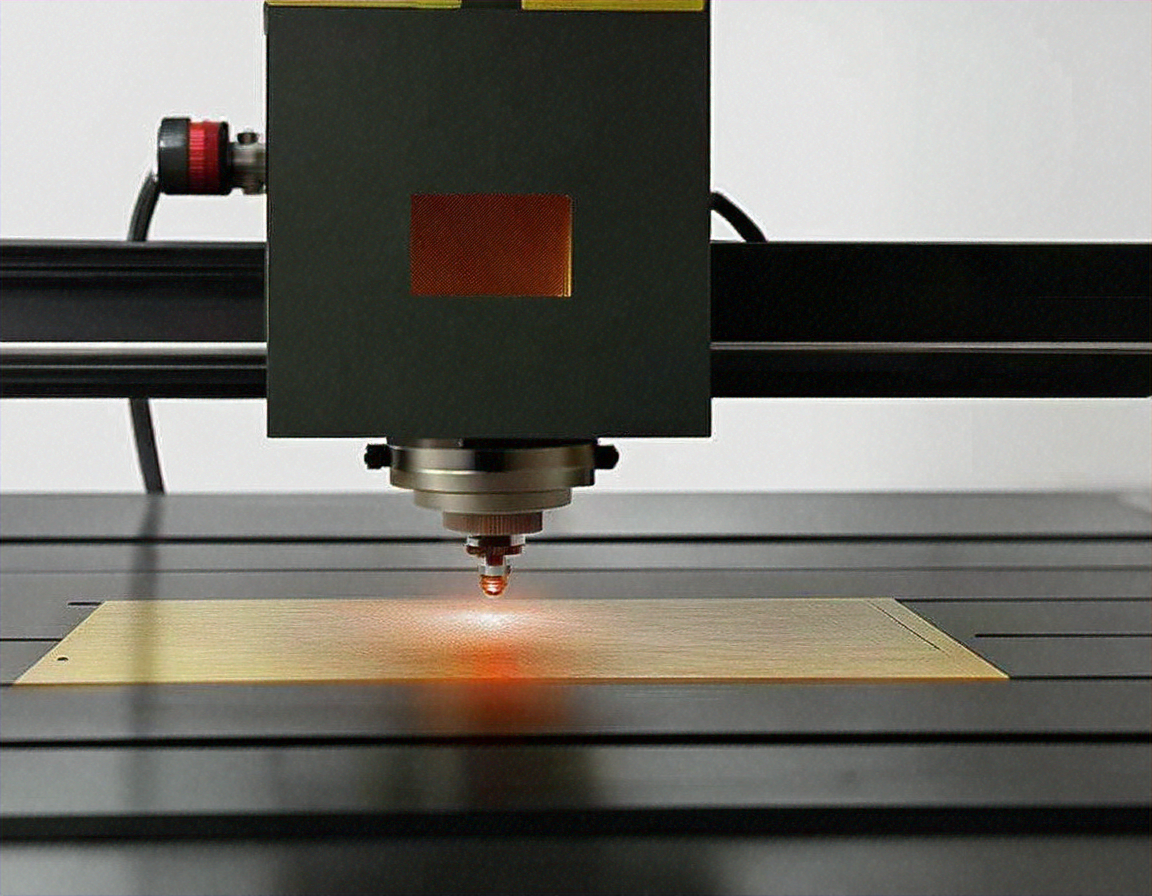
Laser welding has revolutionized manufacturing processes across numerous industries by providing unmatched precision, speed, and quality in joining materials. This advanced technology utilizes concentrated laser energy to melt and fuse materials together, creating strong bonds while minimizing thermal distortion and maintaining excellent aesthetic results.
Learn About Laser Welding Technology
Laser welding operates by focusing a high-intensity laser beam onto the material surface, creating a localized heat source that melts the base materials. The process can be performed in two primary modes: conduction welding for thinner materials and keyhole welding for deeper penetration. The laser beam’s concentrated energy allows for precise control over the welding process, resulting in narrow heat-affected zones and minimal material distortion.
The technology employs various laser types, including fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and diode lasers, each offering specific advantages for different applications. Fiber lasers have gained popularity due to their high beam quality, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements, while CO2 lasers excel in processing thicker materials and non-metallic substances.
The Main Features of Laser Welding Machines
Modern laser welding machines incorporate several key characteristics that distinguish them from conventional welding equipment. High precision stands as the primary advantage, enabling operators to create welds with tolerances measured in micrometers. The non-contact nature of the process eliminates tool wear and reduces contamination risks, particularly important in clean manufacturing environments.
Speed represents another crucial feature, with laser welding capable of achieving welding speeds significantly faster than traditional methods. The process generates minimal spatter and produces clean, smooth welds that often require no post-processing. Additionally, laser welding machines offer excellent repeatability and can be easily integrated into automated production lines, making them ideal for high-volume manufacturing applications.
The flexibility of laser welding systems allows for welding dissimilar materials, including combinations of metals that would be challenging or impossible with conventional techniques. This capability opens new possibilities for product design and material optimization in various industries.
Industrial Applications of Laser Welding
The automotive industry extensively utilizes laser welding for manufacturing body panels, transmission components, and battery assemblies for electric vehicles. The technology’s ability to create strong, lightweight joints while maintaining structural integrity makes it invaluable for modern vehicle production. Aerospace applications include welding turbine components, fuel system parts, and structural elements where precision and reliability are paramount.
Electronics manufacturing relies heavily on laser welding for creating hermetic seals in electronic packages, welding fine wires, and joining components in medical devices. The pharmaceutical and medical device industries benefit from the clean, contamination-free welding process, particularly for surgical instruments and implantable devices.
Jewelry manufacturing has embraced laser welding for its ability to create precise, aesthetically pleasing joints without affecting surrounding gemstones or delicate metalwork. The technology also finds applications in tool manufacturing, where it creates durable cutting edges and repairs worn components.
| Machine Type | Manufacturer | Power Range | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Laser Welder | IPG Photonics | 500W-6kW | $80,000-$300,000 |
| CO2 Laser Welder | Trumpf | 1kW-20kW | $150,000-$800,000 |
| Diode Laser System | Coherent | 100W-2kW | $50,000-$200,000 |
| Handheld Laser Welder | Raycus | 1kW-2kW | $15,000-$50,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Future Trends in Laser Welding
The future of laser welding technology points toward increased automation, artificial intelligence integration, and enhanced process monitoring capabilities. Machine learning algorithms are being developed to optimize welding parameters in real-time, improving quality while reducing setup times. Advanced sensor systems will provide comprehensive process monitoring, enabling predictive maintenance and quality assurance.
Green laser technology is emerging as a solution for welding copper and other highly reflective materials, expanding the range of applications for laser welding. Hybrid processes combining laser welding with other techniques, such as arc welding, are being developed to leverage the advantages of multiple technologies simultaneously.
The integration of Industry 4.0 concepts will enable laser welding systems to communicate with other manufacturing equipment, creating smart factories capable of adaptive production processes. Remote monitoring and control capabilities will allow operators to manage multiple welding stations from centralized locations.
Conclusion
Laser welding technology continues to transform manufacturing processes across diverse industries through its combination of precision, speed, and quality. The technology’s ability to create strong, clean joints while minimizing heat input makes it indispensable for applications requiring high-quality welds. As laser technology advances and costs decrease, adoption will likely expand into new markets and applications, further establishing laser welding as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. The ongoing development of more powerful, efficient, and intelligent laser welding systems promises to unlock new possibilities for product design and manufacturing optimization in the years ahead.