Exploring Design Elements and Features of Modern Houses
As we move into 2026, the design of modern houses reflects a blend of style and sustainability that resonates with American values. From open floor plans popularized by HGTV to smart home technology reflecting California innovation, discover how these elements shape contemporary life, offering comfort and efficiency for families across the nation.
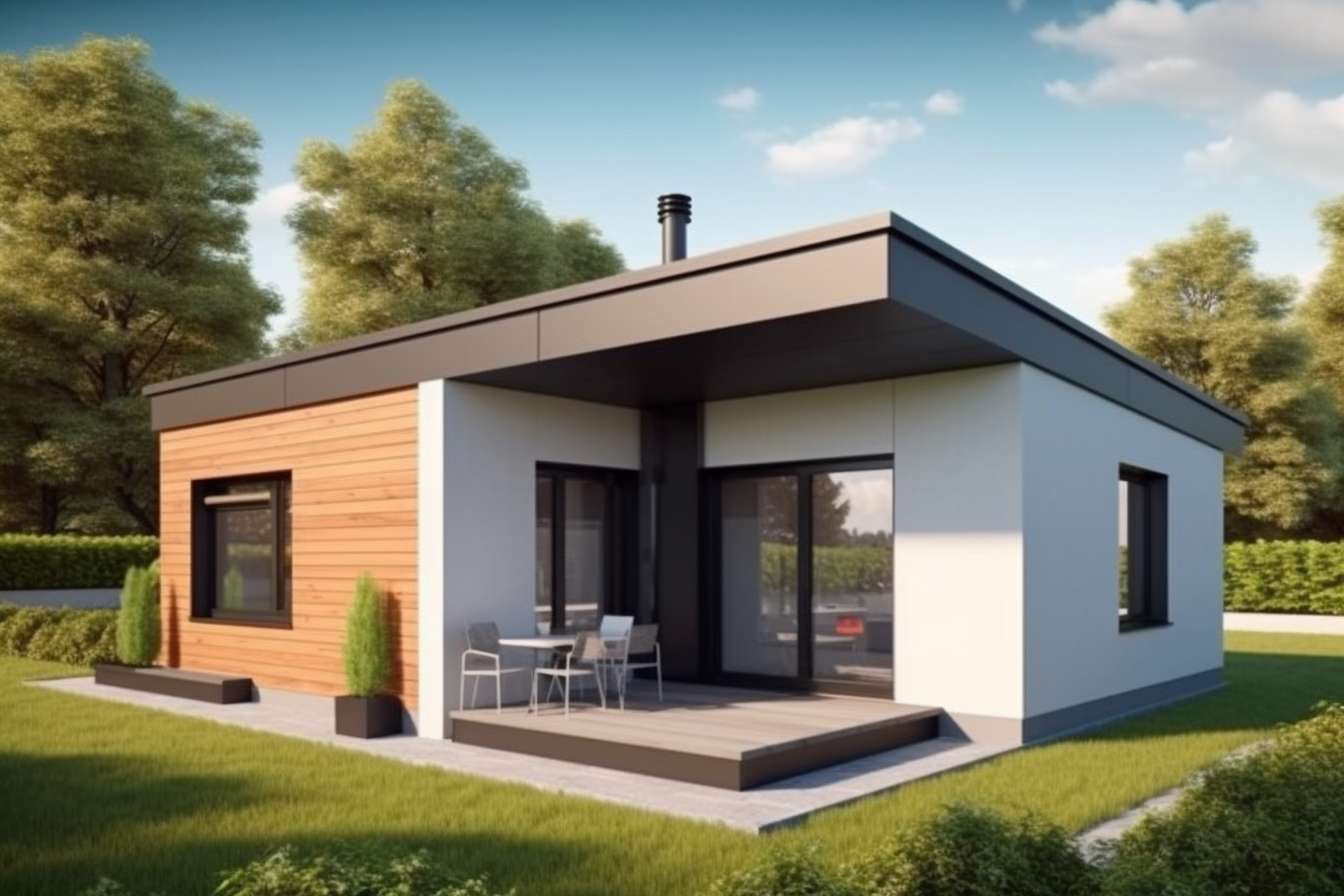

Contemporary residential design has evolved significantly over recent decades, shaped by changing lifestyles, technological advances, and environmental consciousness. Modern houses showcase distinctive characteristics that set them apart from traditional architectural approaches, emphasizing clean lines, functional spaces, and seamless integration between indoor and outdoor environments. These homes reflect a philosophy that values simplicity, efficiency, and connection to the surrounding landscape while incorporating innovations that enhance daily living.
The Impact of Open Floor Plans
Open floor plans have become a defining characteristic of contemporary residential design, fundamentally changing how families interact within their homes. This layout approach removes walls between kitchen, dining, and living areas, creating expansive, multifunctional spaces that encourage social interaction and flexibility. The absence of physical barriers allows natural light to penetrate deeper into the home, reducing dependence on artificial lighting during daytime hours. Open layouts also provide visual continuity, making homes feel more spacious even within modest square footage. Families appreciate the ability to supervise children while preparing meals or to entertain guests without isolation from the main gathering areas. However, this design approach requires thoughtful furniture placement and acoustic considerations to maintain functional zones while preserving the sense of openness that makes these layouts appealing.
Sustainable Features in Modern Homes
Environmental responsibility has become central to contemporary residential construction, with sustainable features now standard rather than optional in many new builds. Energy-efficient windows with low-emissivity coatings minimize heat transfer, reducing heating and cooling costs throughout the year. Solar panel installations have become increasingly common, allowing homeowners to generate renewable energy and reduce reliance on traditional power grids. Water conservation systems including low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting, and greywater recycling help minimize resource consumption. Insulation technology has advanced considerably, with spray foam and structural insulated panels providing superior thermal performance compared to traditional materials. Many modern homes incorporate passive solar design principles, positioning windows and overhangs to maximize winter heat gain while minimizing summer solar exposure. Sustainable building materials such as reclaimed wood, recycled metal roofing, and rapidly renewable bamboo flooring reduce environmental impact without compromising aesthetic appeal or structural integrity.
Smart Home Technology Trends
Technological integration has transformed modern houses into responsive environments that adapt to occupant preferences and behaviors. Smart thermostats learn household patterns and adjust temperature settings automatically, optimizing comfort while reducing energy consumption. Lighting systems respond to natural daylight levels and occupancy, dimming or brightening as needed without manual intervention. Security systems now offer remote monitoring through smartphone applications, allowing homeowners to view camera feeds and control door locks from anywhere with internet connectivity. Voice-activated assistants integrate multiple systems, enabling hands-free control of entertainment, climate, and lighting through simple verbal commands. Automated window treatments adjust throughout the day to manage solar heat gain and privacy. Smart appliances communicate with utility providers to operate during off-peak hours, reducing electricity costs. Home automation hubs consolidate control of disparate systems into unified interfaces, simplifying management of increasingly complex residential technology ecosystems. These innovations enhance convenience while providing data insights that help homeowners optimize resource usage and identify maintenance needs before they become serious problems.
Influential Architectural Styles
Several architectural movements have shaped contemporary residential design, each contributing distinct aesthetic and functional elements. Mid-century modern architecture, experiencing renewed popularity, emphasizes horizontal lines, flat or gently sloping roofs, and extensive glass walls that blur boundaries between interior and exterior spaces. Minimalist design principles focus on simplicity and reduction, featuring unadorned surfaces, neutral color palettes, and careful attention to proportion and material quality. Industrial aesthetics incorporate exposed structural elements, metal fixtures, and raw materials like concrete and brick, celebrating functional beauty. Scandinavian design influences bring warmth through natural wood tones, textured textiles, and cozy atmospheres despite minimal ornamentation. Contemporary farmhouse style blends rustic elements with modern conveniences, featuring board-and-batten siding, metal roofs, and open interior layouts. These diverse influences often merge within individual projects, creating eclectic yet cohesive designs that reflect personal taste while maintaining contemporary sensibilities. Architects and designers draw selectively from these traditions, adapting historical precedents to current needs and technologies.
Creating Outdoor Living Spaces
Modern residential design extends living areas beyond traditional interior boundaries, treating outdoor spaces as essential components of the home rather than afterthoughts. Covered patios and pergolas provide weather protection while maintaining connection to the landscape, effectively expanding usable square footage during favorable weather. Outdoor kitchens equipped with grills, refrigerators, and counter space enable complete meal preparation without returning indoors. Fire pits and outdoor fireplaces create gathering points that extend outdoor season usage into cooler months. Thoughtful landscaping incorporates native plants that require minimal irrigation and maintenance while providing visual interest and habitat for local wildlife. Hardscaping elements including stone pathways, retaining walls, and decorative pavers define outdoor rooms and manage water drainage. Lighting design extends functionality into evening hours, illuminating pathways for safety while creating ambiance through strategic placement of fixtures. Pool areas often feature infinity edges or natural designs that integrate with surrounding landscapes. These outdoor extensions reflect lifestyle priorities that value fresh air, natural light, and connection to the environment as integral to daily living rather than occasional luxuries.
Conclusion
The design elements and features that define modern houses reflect broader cultural shifts toward openness, sustainability, and technological integration. Open floor plans facilitate family interaction and spatial efficiency, while sustainable features address environmental concerns and reduce operational costs. Smart home technology enhances convenience and resource management, and diverse architectural influences provide aesthetic richness. Outdoor living spaces extend the functional footprint of homes, creating seamless transitions between built and natural environments. Together, these elements create residential environments that respond to contemporary needs while anticipating future developments in how we inhabit and interact with our homes. Understanding these design principles helps individuals make informed decisions whether building new, renovating existing properties, or simply appreciating the thoughtful planning behind contemporary residential architecture.