Factors Affecting Current Construction and Mortgage Interest Rates
Explore the key factors driving current construction and mortgage interest rates in Germany, including ECB policy and inflation trends, housing supply and demand, regional construction and material costs, borrower creditworthiness, and loan-to-value ratios. Learn how fixed vs. variable rates differ, what to watch when refinancing, and practical steps buyers and homeowners can take to secure more favorable mortgage terms.
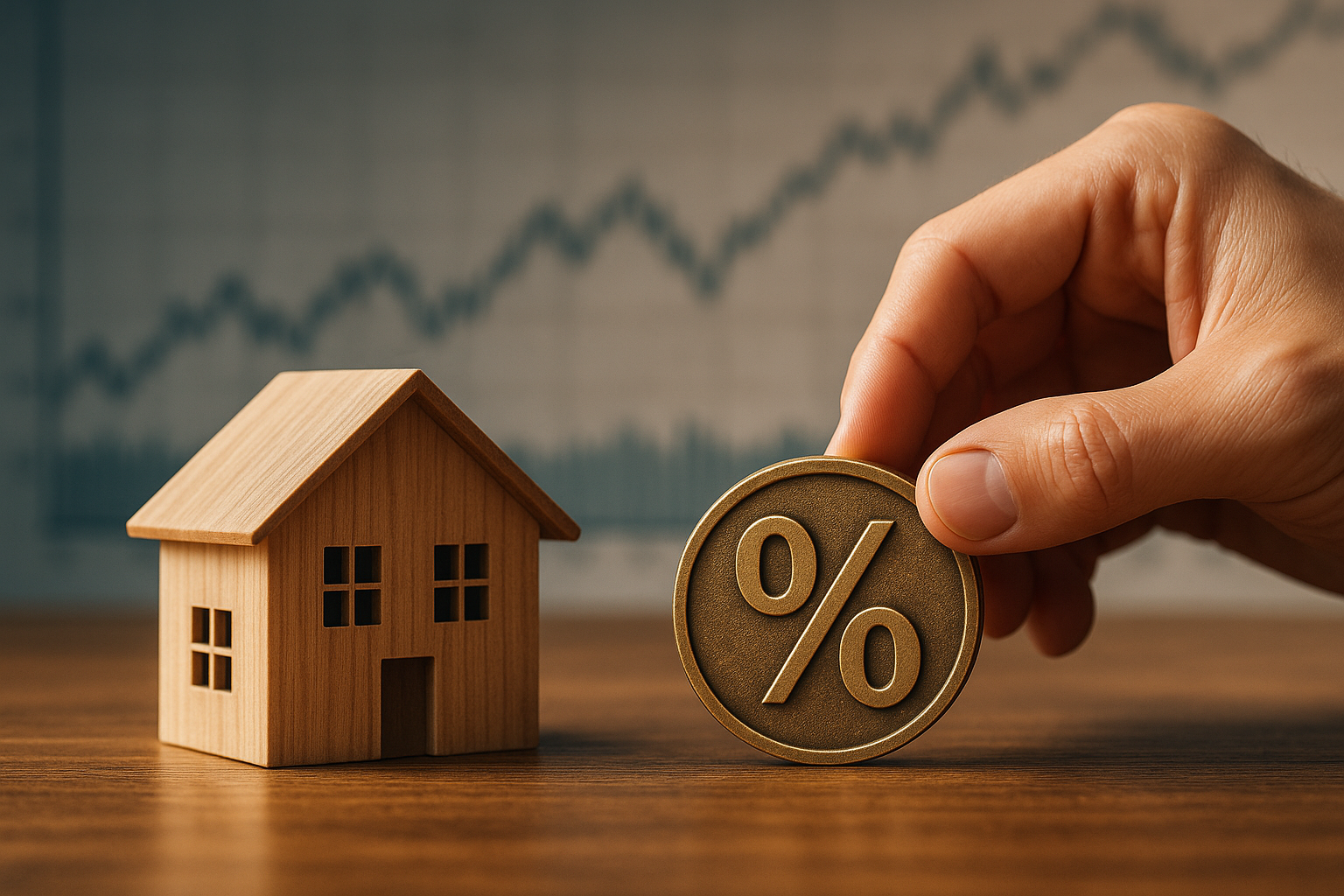

Interest rates on construction loans and mortgages represent one of the most significant financial considerations for property development and homeownership. These rates are influenced by a complex interplay of economic, regulatory, and market-specific factors that can vary considerably across different regions and time periods.
ECB Policy and Inflation Trends Impact on Borrowing Costs
The European Central Bank’s monetary policy decisions serve as the foundation for interest rate movements across the eurozone. When the ECB adjusts its key interest rates, commercial banks typically respond by modifying their lending rates accordingly. Inflation trends play a particularly crucial role, as central banks often raise rates to combat rising prices, making borrowing more expensive. Conversely, during periods of low inflation or economic uncertainty, rates may be lowered to stimulate economic activity. These policy shifts directly affect the cost of capital for both construction projects and residential mortgages, with changes often taking several months to fully permeate the lending market.
Housing Supply and Demand Dynamics
Market fundamentals significantly influence lending conditions and interest rate premiums. Areas experiencing high housing demand relative to available supply often see increased competition among lenders, potentially leading to more favorable rates for qualified borrowers. Conversely, markets with oversupply or declining demand may result in tighter lending standards and higher risk premiums. Population growth, employment opportunities, and urban development patterns all contribute to these supply-demand imbalances. Lenders assess these regional factors when determining risk levels and appropriate pricing for construction and mortgage loans.
Regional Construction and Material Costs
Construction financing rates are particularly sensitive to regional building costs and material price volatility. Areas with higher construction costs often see elevated interest rates on development loans, as lenders factor in increased project risks and longer completion timelines. Material price fluctuations, labor shortages, and regulatory compliance costs all influence the overall risk profile of construction projects. Lenders may adjust rates based on local market conditions, with regions experiencing rapid cost increases potentially facing higher borrowing costs to account for budget overrun risks.
Borrower Creditworthiness and Loan-to-Value Considerations
Individual borrower characteristics play a fundamental role in determining specific interest rates offered. Credit scores, debt-to-income ratios, employment stability, and down payment amounts all influence lending decisions. Loan-to-value ratios are particularly important, with lower ratios typically resulting in more favorable rates due to reduced lender risk exposure. Borrowers with strong financial profiles may qualify for premium rates, while those with higher risk factors face rate premiums. Documentation requirements, income verification standards, and collateral evaluation processes all contribute to the final rate determination.
Fixed vs Variable Rates and Refinancing Strategies
The choice between fixed and variable rate structures significantly impacts long-term borrowing costs and risk exposure. Fixed rates provide payment stability but may be higher initially to compensate for interest rate risk. Variable rates often start lower but expose borrowers to future rate increases. Refinancing opportunities allow borrowers to potentially reduce costs when market conditions improve, though transaction costs and qualification requirements must be considered. Timing refinancing decisions requires careful analysis of rate trends, remaining loan terms, and individual financial circumstances.
| Lender Type | Typical Rate Range | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Banks | 3.5% - 5.2% | Comprehensive services, established relationships |
| Credit Unions | 3.2% - 4.8% | Member benefits, competitive rates |
| Online Lenders | 3.4% - 5.5% | Streamlined processes, digital convenience |
| Specialized Construction Lenders | 4.0% - 6.0% | Industry expertise, flexible terms |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Understanding these interconnected factors enables borrowers to make more informed decisions about timing, loan structure, and lender selection. Market conditions, policy environments, and individual circumstances all contribute to the complex landscape of construction and mortgage interest rates. Successful navigation requires ongoing monitoring of economic indicators, regional market trends, and personal financial positioning to optimize borrowing strategies and minimize long-term costs.