Senior Rental Hub
Looking to rent a senior apartment near you? This rental-focused guide shows you how to find available units, compare lease terms and monthly costs, understand what's included in senior housing rentals, and identify income-based rental programs in your area.
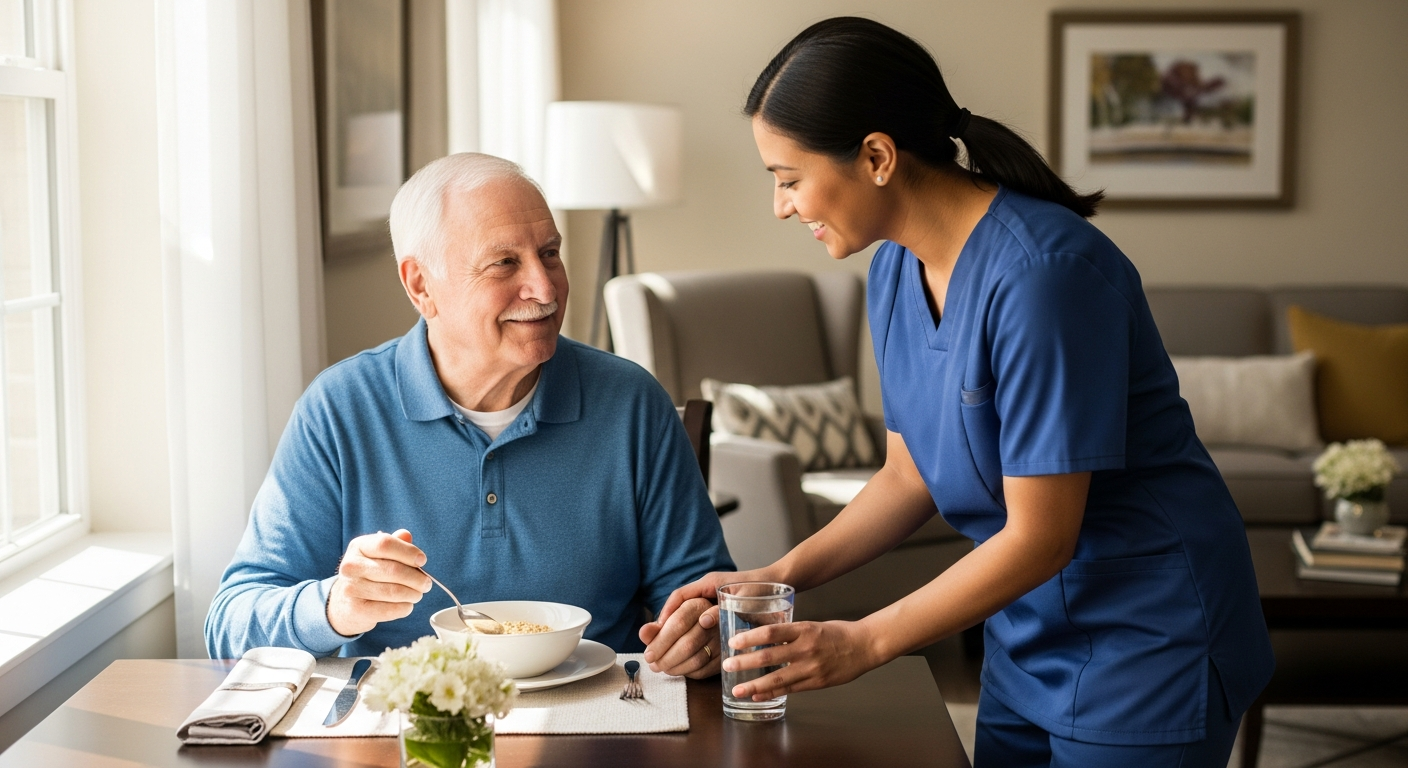

What Types of Housing Are Available for Older Adults?
Older adults have access to several housing arrangements designed to meet varying needs and preferences. Independent living communities offer apartment-style living with minimal assistance, typically featuring amenities like fitness centers, social activities, and maintenance services. These communities allow residents to maintain their independence while providing a supportive environment.
Assisted living facilities provide more comprehensive support, including help with daily activities like medication management, bathing, and meal preparation. Memory care units specialize in caring for individuals with dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, offering secure environments with specialized staff training.
Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRCs) provide a continuum of care, allowing residents to transition between independent living, assisted living, and skilled nursing care as their needs change. Adult family homes offer smaller, residential settings with personalized care, while naturally occurring retirement communities (NORCs) are neighborhoods where many residents have aged in place.
How Do Income-Based Housing Programs Work?
Income-based housing programs help older adults with limited financial resources access affordable accommodations. The Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) administers several programs specifically for seniors, including Section 202 Supportive Housing for the Elderly and Section 8 Housing Choice Vouchers.
Section 202 provides rental assistance and supportive services in developments specifically designed for low-income elderly residents. Eligibility typically requires being 62 years or older and having income at or below 50% of the area median income. These properties often include features like wheelchair accessibility, emergency call systems, and coordinated services.
Section 8 vouchers allow eligible seniors to choose their housing in the private market, with the program paying a portion of the rent directly to landlords. The Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) program also creates affordable rental housing, with some properties designated specifically for seniors.
Public housing authorities maintain waiting lists for these programs, and application processes vary by location. Priority is often given to those with extremely low incomes, disabilities, or who are currently homeless.
What Should You Look for When Searching Locally?
When searching for senior housing in your area, several factors deserve careful consideration. Location plays a crucial role, including proximity to healthcare facilities, public transportation, shopping centers, and family members. Evaluate the neighborhood’s walkability and safety, as these directly impact daily life quality.
Financial considerations extend beyond monthly rent or fees. Understand what services are included in the base cost and which require additional payments. Some communities charge entrance fees, while others operate on a monthly rental basis. Review contract terms carefully, including policies on fee increases and refund procedures.
Tour potential communities during different times of day to observe activity levels and staff interactions. Ask about staff-to-resident ratios, employee background checks, and training requirements. Inquire about meal programs, transportation services, and social activities that align with your interests and needs.
Check licensing and inspection records through state regulatory agencies. Online reviews and speaking with current residents or their families can provide valuable insights into daily life and satisfaction levels.
| Housing Type | Average Monthly Cost | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Independent Living | $2,500 - $4,500 | Apartment-style, minimal assistance, amenities |
| Assisted Living | $3,500 - $6,500 | Personal care services, meals, medication help |
| Memory Care | $4,500 - $8,000 | Specialized dementia care, secure environment |
| Adult Family Home | $3,000 - $5,500 | Small residential setting, personalized care |
| Section 202 Housing | $300 - $800 | Income-based rent, supportive services |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
How Do Independent Living Apartments Differ from Other Options?
Independent living apartments cater to active older adults who can manage daily activities without assistance but desire a community environment with conveniences and social opportunities. Unlike assisted living facilities, independent living communities don’t provide personal care services like help with bathing, dressing, or medication management.
Residents in independent living typically maintain their own apartments or condominiums with full kitchens, allowing them to prepare their own meals if desired. However, many communities offer optional meal plans and dining facilities. Housekeeping and maintenance services are commonly included, freeing residents from home upkeep responsibilities.
These communities emphasize social engagement through organized activities, clubs, fitness programs, and educational opportunities. Transportation services may be available for shopping trips, medical appointments, and community outings. Some independent living communities are part of larger retirement complexes that include assisted living and skilled nursing facilities, allowing residents to transition to higher levels of care if needed.
The main distinction lies in the level of independence maintained. Residents come and go as they please, have visitors without restrictions, and maintain their privacy while benefiting from community amenities and social connections. This option works well for individuals who are healthy and active but want to downsize from homeownership or live in a more social environment.
Choosing appropriate housing as an older adult requires careful evaluation of current needs, future considerations, and available resources. Whether exploring independent living communities, applying for income-based assistance, or comparing local options, taking time to research and visit potential communities ensures better long-term satisfaction. Understanding the differences between housing types and available support programs empowers older adults to make informed decisions that enhance their quality of life while maintaining their preferred level of independence.