Understanding Affordable Energy-Efficient Prefabricated Homes in the US (2026)
Prefabricated homes in the United States combine factory-built components with on-site assembly to shorten construction timelines and reduce material waste. This article explains core concepts, installation processes, cost factors, energy performance, and environmental implications relevant to 2026.
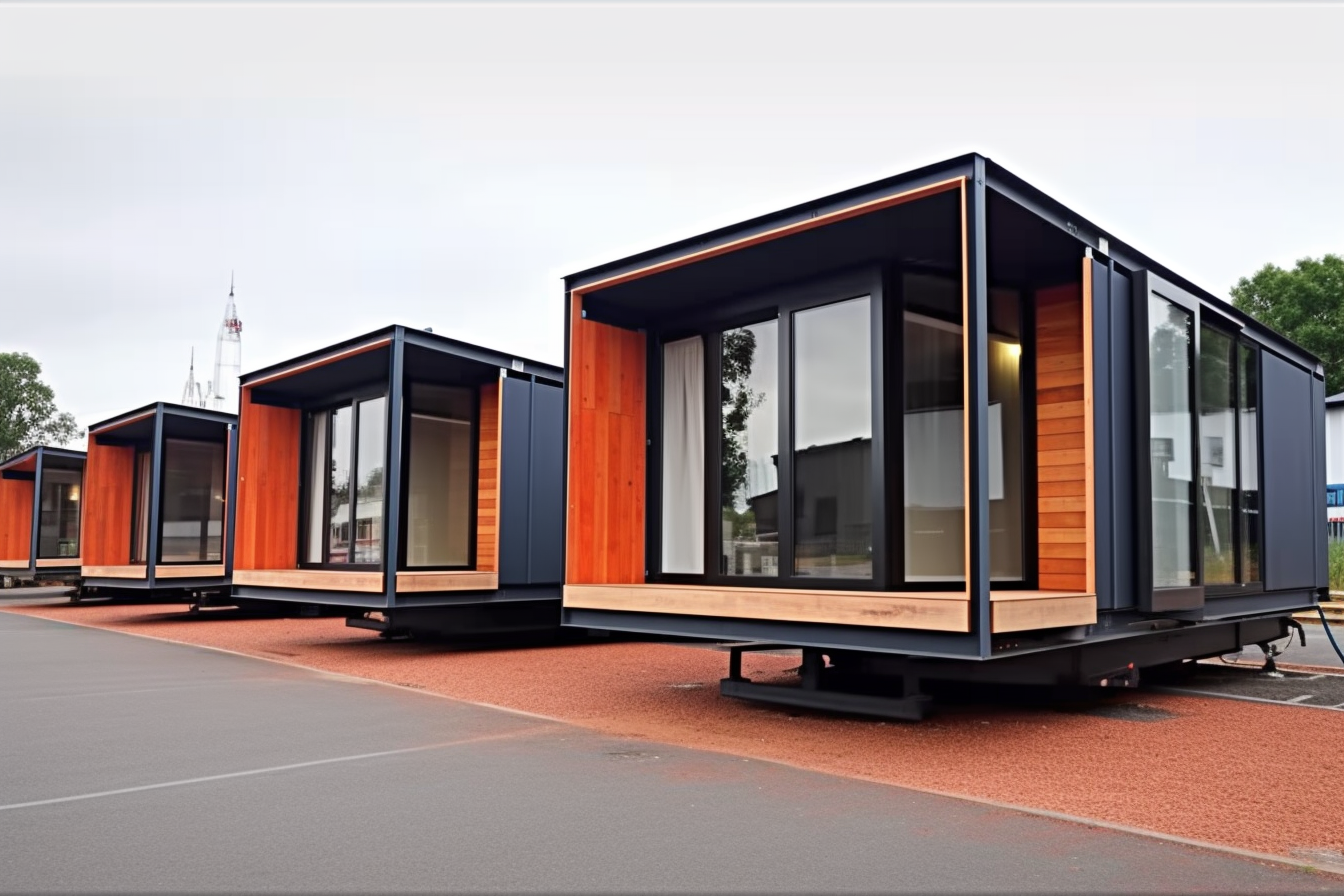

What Are Prefabricated Homes and Their Growing Appeal?
Prefabricated homes, often referred to as prefab homes, are structures or components of structures built off-site in a controlled factory environment. These components, which can range from individual wall panels to entire modular sections, are then transported to the building site for assembly. This method contrasts sharply with traditional stick-built construction, where the entire process occurs on location. The growing appeal of prefabricated homes stems from several key advantages, including enhanced quality control due to factory conditions, reduced construction timelines, and the potential for significant cost savings, making them an attractive option for homeowners seeking efficiency and value.
Streamlining Construction: Shorter On-Site Installation Processes
One of the most notable benefits of prefabricated construction is the dramatically shorter on-site installation time. Because major components or modules are manufactured simultaneously with site preparation (like foundation laying), the on-site phase primarily involves assembly. This streamlined process minimizes delays caused by adverse weather conditions, reduces the need for extensive on-site labor, and lessens disruption to the surrounding community. Once the modules arrive, they are craned into place and connected, often completing the structural shell of a home in days or weeks rather than months.
Cost Reduction Strategies in Prefabricated Home Construction
Prefabricated homes often present a more cost-effective path to homeownership. The factory setting allows for economies of scale in material purchasing, as builders can buy materials in bulk at lower prices. Waste is also significantly reduced during the manufacturing process, contributing to savings. Furthermore, the efficiency of factory production and the shorter on-site assembly time lead to reduced labor costs and lower financing expenses for the construction period. While initial costs for the home module can vary, the overall project cost can be more predictable and often lower than a comparable site-built home, especially when considering time savings and reduced waste.
Enhancing Sustainability: Energy Efficiency in Prefabricated Homes
Energy efficiency is a core advantage of many prefabricated homes. The controlled environment of a factory allows for precise construction techniques, leading to tighter building envelopes, superior insulation installation, and reduced thermal bridging. This meticulous approach results in homes that are better sealed and insulated than many traditional builds, significantly lowering heating and cooling costs for residents. Many prefab manufacturers also integrate advanced energy-saving features, such as high-performance windows, efficient HVAC systems, and options for solar panel readiness, further enhancing their environmental performance and long-term affordability.
Reducing Environmental Impact Through Minimized Construction Waste
The construction industry is known for generating substantial waste. Prefabricated construction offers a compelling solution by significantly minimizing this environmental impact. In a factory setting, materials are cut to precise specifications, and leftover scraps can be more easily collected, recycled, or repurposed. This efficient use of resources drastically reduces the amount of material sent to landfills compared to traditional construction sites, where waste management can be more challenging. This commitment to waste reduction aligns with broader sustainability goals and contributes to a more environmentally responsible building process.
Understanding the potential costs associated with prefabricated homes involves considering various factors beyond the basic module price. These include land acquisition, foundation work, utility hookups, permitting fees, transportation of modules, and site-specific preparations. While the factory-built component can offer cost savings, the total project cost will vary based on location, design complexity, and local labor rates. The estimates below focus on the cost of the home module itself, excluding these additional site-related expenses.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation (Home Module Only) |
|---|---|---|
| Manufactured/Modular Homes | Clayton Homes | Starting from $50,000 - $150,000+ |
| Modern Prefab Homes | Blu Homes | Starting from $300,000 - $500,000+ |
| Custom Prefab Homes | Method Homes | Starting from $250,000 - $450,000+ |
| Contemporary Prefab Homes | Connect Homes | Starting from $200,000 - $400,000+ |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
In summary, prefabricated homes present a forward-thinking approach to construction that offers numerous advantages for homeowners in the United States. Their streamlined production, potential for cost savings, inherent energy efficiency, and commitment to minimizing construction waste make them an increasingly viable and attractive option in the modern housing market. As building technologies continue to advance, the role of prefabricated construction in providing accessible and sustainable housing solutions is expected to grow, shaping the future of residential development across the country.