Understanding How Alarm Systems Work at Home
Alarm systems use different parts like sensors, lights, and sounds to let people know when something changes in a house. Learning how these parts work together can help you understand technology that can notice unusual events and respond automatically.
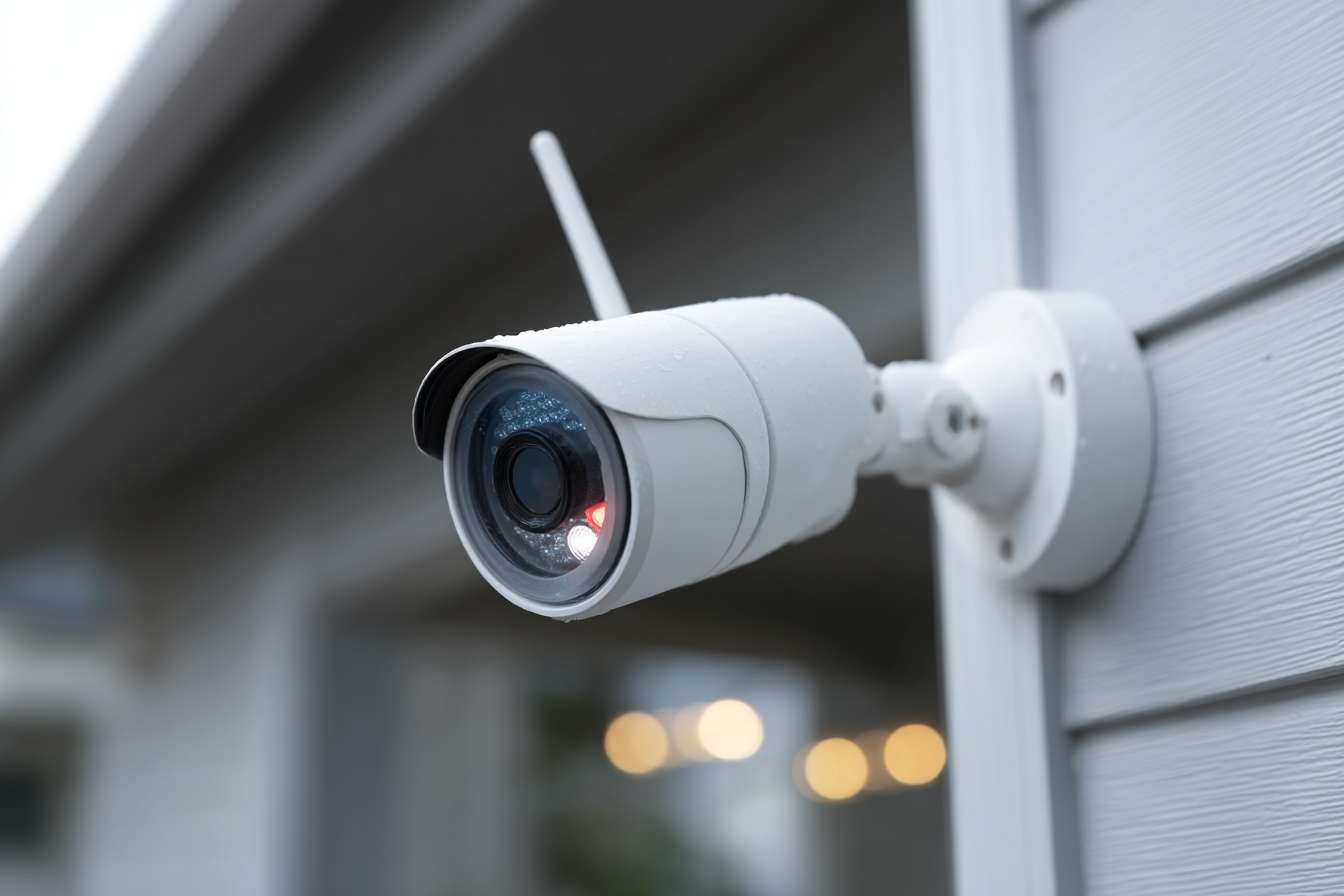

Home security systems have evolved significantly from simple door chimes to comprehensive networks that integrate multiple detection methods and communication technologies. These systems create protective barriers around your property by monitoring entry points, detecting motion, and identifying environmental hazards like smoke or carbon monoxide.
Components of Home Security Technology
A typical residential security system consists of several interconnected components working in harmony. The control panel serves as the central hub, processing signals from various sensors and triggering appropriate responses. Door and window sensors use magnetic contacts to detect when entry points are opened, while motion detectors use infrared technology to identify movement within protected areas.
Glass break sensors listen for the specific frequency patterns created when windows shatter, and smoke detectors monitor air quality for signs of fire. Modern systems also include keypads for user interaction, sirens for audible alerts, and backup batteries to maintain operation during power outages. Each component communicates wirelessly or through hardwired connections to create a comprehensive security network.
How Residential Alert Systems Detect Threats
Threat detection relies on multiple sensor technologies that monitor different aspects of your home environment. Passive infrared sensors detect body heat and movement patterns, distinguishing between normal household activity and potential intrusions. Dual-technology motion detectors combine infrared and microwave sensors to reduce false alarms while maintaining high sensitivity to actual threats.
Door and window sensors create invisible security perimeters by monitoring the magnetic field between sensor components. When a protected entry point opens, the magnetic connection breaks, triggering an immediate alert. Advanced sensors can differentiate between authorized entries using proper disarm codes and unauthorized access attempts.
Smart Home Sensors and Integration Options
Contemporary security systems integrate seamlessly with smart home ecosystems, allowing homeowners to control multiple devices through unified interfaces. Smart sensors can communicate with lighting systems, thermostats, and door locks to create automated responses to security events. For example, motion detection can trigger pathway lighting, while security breaches can automatically lock all smart locks throughout the home.
Wireless sensors eliminate the need for extensive wiring during installation and provide flexibility for system expansion. These devices use encrypted communication protocols to prevent signal interception and maintain secure connections with the central control panel. Battery-powered sensors include low-battery alerts to ensure continuous protection.
Home Monitoring Devices and Remote Access
Modern security systems provide real-time monitoring capabilities through smartphone applications and web portals. Homeowners can arm or disarm their systems remotely, receive instant notifications about security events, and view live camera feeds from anywhere with internet access. These monitoring capabilities extend beyond basic security functions to include environmental monitoring for temperature changes, water leaks, and air quality issues.
Professional monitoring services complement self-monitoring options by providing 24/7 oversight from trained security personnel. When alarms trigger, monitoring centers verify the emergency and coordinate appropriate responses, including contacting homeowners, emergency services, or designated contacts based on predetermined protocols.
Electronic Warning Systems and Alert Protocols
Alert protocols determine how systems respond to different types of security events. Silent alarms notify monitoring services without alerting potential intruders, while audible sirens serve as deterrents and neighborhood alerts. Systems can be programmed with different response levels for various zones, allowing gentle chimes for interior motion during occupied hours while maintaining full security for perimeter breaches.
Modern systems support multiple communication methods to ensure reliable alert delivery. Primary communication typically occurs through broadband internet connections, with cellular backup maintaining connectivity during internet outages. Some systems include landline backup as a third communication layer for maximum reliability.
| System Type | Provider | Monthly Cost | Installation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Monitored | ADT | $45-60 | $99-199 |
| Smart Home Integration | Vivint | $50-80 | $199-299 |
| DIY Professional | Ring Alarm | $10-20 | $199-299 |
| Self-Monitored | SimpliSafe | $15-25 | $244-344 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Understanding how these systems function helps homeowners optimize their security configurations and respond appropriately to different alert types. Regular system testing and maintenance ensure all components remain functional and provide reliable protection. As technology continues advancing, these systems become increasingly sophisticated while remaining user-friendly for everyday operation.